BCI-Controlled Hands-Free Wheelchair Navigation with Obstacle Avoidance
Ramy Mounir, Redwan Alqasemi, Rajiv Dubey
Abstract
Brain-Computer interfaces (BCI) are widely used in reading brain signals and converting them into real-world motion. However, the signals produced from the BCI are noisy and hard to analyze. This paper looks specifically towards combining the BCI's latest technology with ultrasonic sensors to provide a hands-free wheelchair that can efficiently navigate through crowded environments.
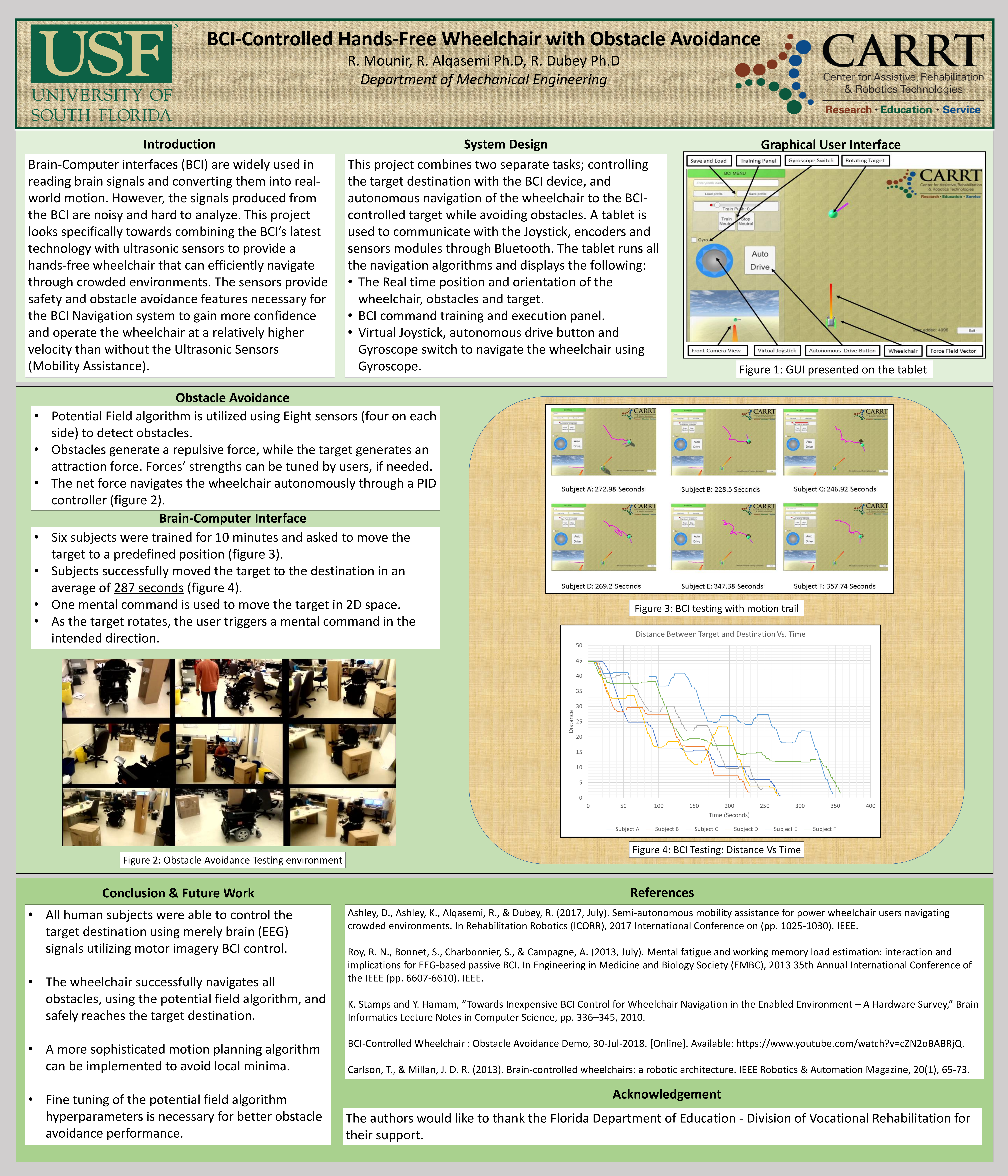
Approach
We fuse signals from different sensors to achieve better performance in obstacle avoidance. An array of 10 ultrasonic sensors are used along with the results of indoor segmentation to detect obstacles and navigate around them.
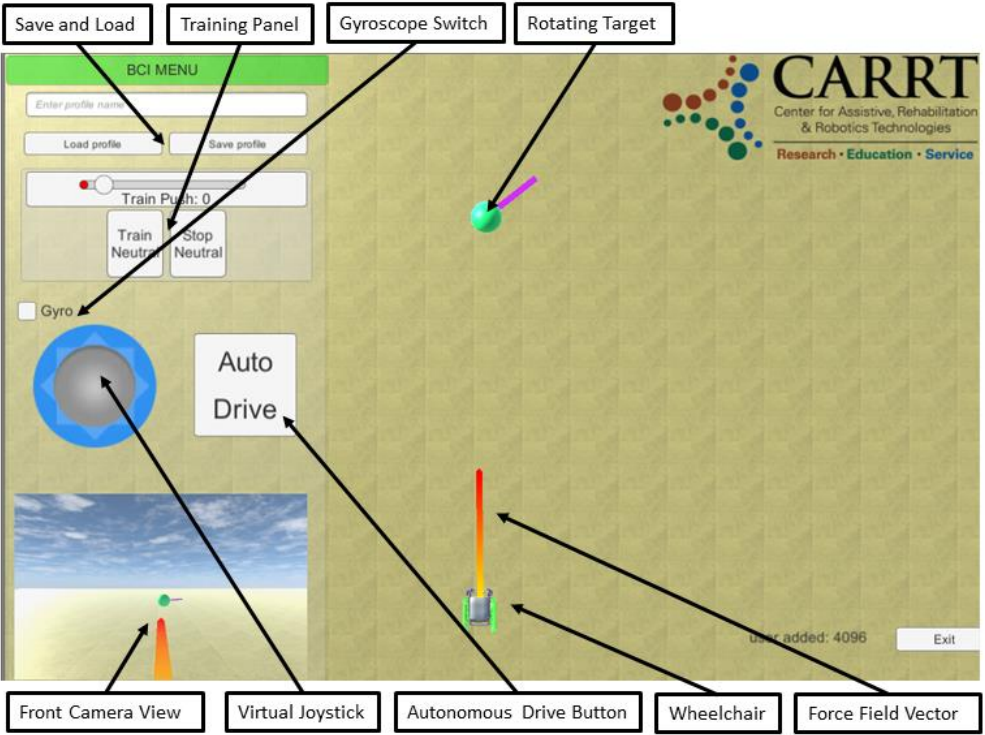
Subjects were able to successfully navigate the target to the destination. The distance continued to decrease with time, zero distance means that the target has reached its destination.
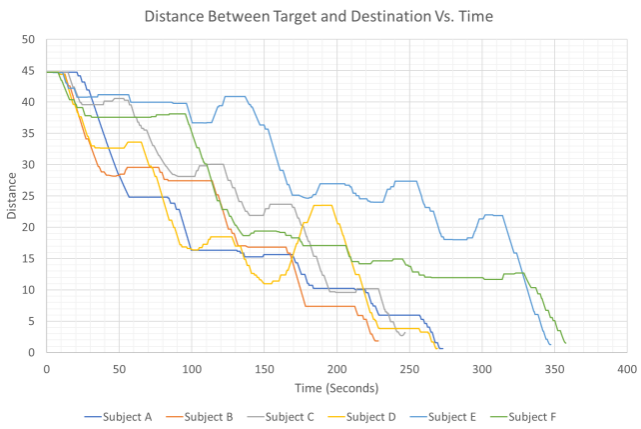
The path of each target as controlled by the human subjects.
Poster
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Florida Department of Education - Division of Vocational Rehabilitation.
Citation
@misc{bci,
title = {BCI-Controlled Hands-Free Wheelchair Navigation with Obstacle Avoidance},
author = {Ramy Mounir and Redwan Alqasemi and Rajiv Dubey},
booktitle = {International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems Workshop},
year = {2018},
note = {IROS}
}